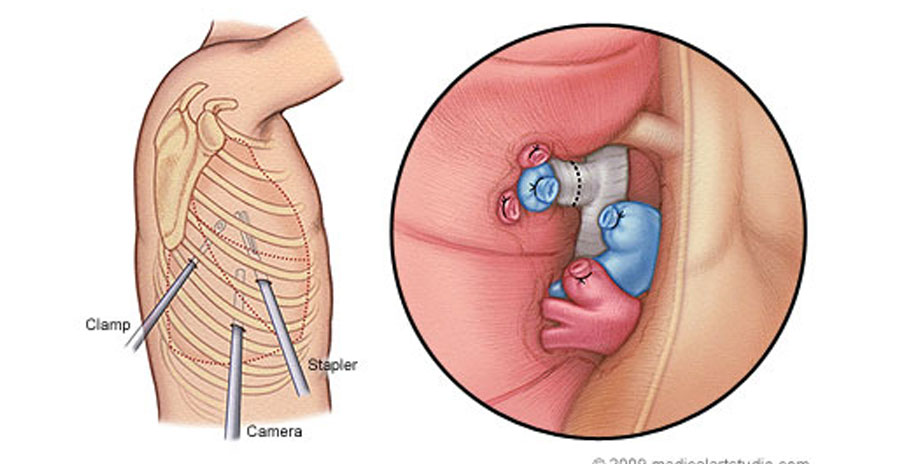
Chest and VATS (Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery) surgery involve procedures performed on the organs and structures within the chest cavity, including the lungs, esophagus, and mediastinum. These surgeries are typically performed to diagnose and treat a wide range of thoracic conditions, including lung cancer, pleural effusions, empyema, pneumothorax, esophageal disorders, and mediastinal tumors.
VATS is a minimally invasive surgical technique that uses small incisions and a thoracoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera and surgical instruments) to access the chest cavity. This approach allows surgeons to visualize and operate on the thoracic organs with greater precision and less trauma to surrounding tissues compared to traditional open surgery.
Chest and VATS surgeries may involve various procedures, such as lung biopsy, lobectomy (removal of a lobe of the lung), wedge resection, mediastinal tumor resection, esophageal myotomy (for achalasia), and pleurodesis (for recurrent pleural effusions).
Advantages of VATS surgery include shorter hospital stays, faster recovery times, reduced postoperative pain, and improved cosmetic outcomes compared to open surgery. However, not all thoracic conditions are suitable for VATS, and the appropriate surgical approach depends on factors such as the patient's condition, the nature of the disease, and the surgeon's expertise.
Copyright © 2024, Dr. Chandrakant Sabale, All Rights Reserved.