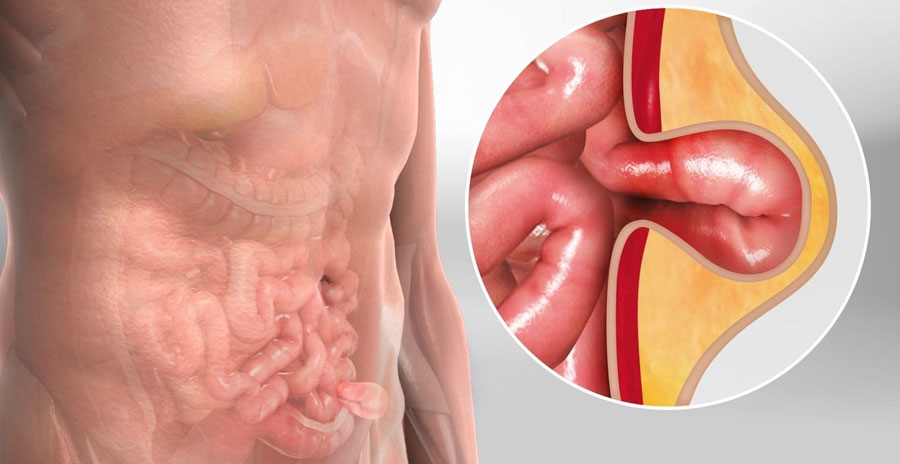
Hernia surgery, also known as herniorrhaphy or hernioplasty, is a common surgical procedure performed to repair a hernia, which occurs when an organ or fatty tissue protrudes through a weak spot or tear in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue. Hernias can develop in various areas of the body, with the most common types being inguinal (groin), femoral (upper thigh), umbilical (belly button), and incisional (at the site of a previous surgical incision).
During hernia surgery, the protruding tissue is pushed back into place, and the weakened area of the muscle or tissue is reinforced or repaired. The surgical approach may involve traditional open surgery or minimally invasive techniques such as laparoscopic surgery or robotic-assisted surgery. In laparoscopic or robotic-assisted procedures, small incisions are made, and a camera and specialized instruments are used to perform the repair with precision.
Hernia surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia and is considered a safe and effective treatment for hernias. Most patients can return home the same day or within a day or two after surgery, with minimal discomfort and a relatively quick recovery period. Following surgery, patients are advised to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities to allow for proper healing of the repaired tissue. Overall, hernia surgery helps alleviate symptoms and reduces the risk of complications associated with untreated hernias, improving patients' quality of life.
Copyright © 2024, Dr. Chandrakant Sabale, All Rights Reserved.